Our system features a fully ROS-integrated robot designed for versatile applications, with a primary focus on testing multi-agent algorithms. This system was developed to participate in the national-level FlipKart Grid 3.0 Robotics Challenge 2021.
We built the platform and integrated ROS with the robot, utilizing Apriltag_ros and an array of cameras for localization. Additionally, we implemented autonomous navigation and optimal path computation, taking into account the presence of other robots in the arena. The complete package, including the controller and planner, is available on our Dot-Bot GitHub repository.
Robot Control
The robot's control architecture employs a state-of-the-art implementation using both a microprocessor and a microcontroller. Sensor fusion techniques are utilized for precise position estimation, complemented by external cameras that detect Apriltags marking the robot's position. The control architecture is illustrated below and further detailed in the following points:
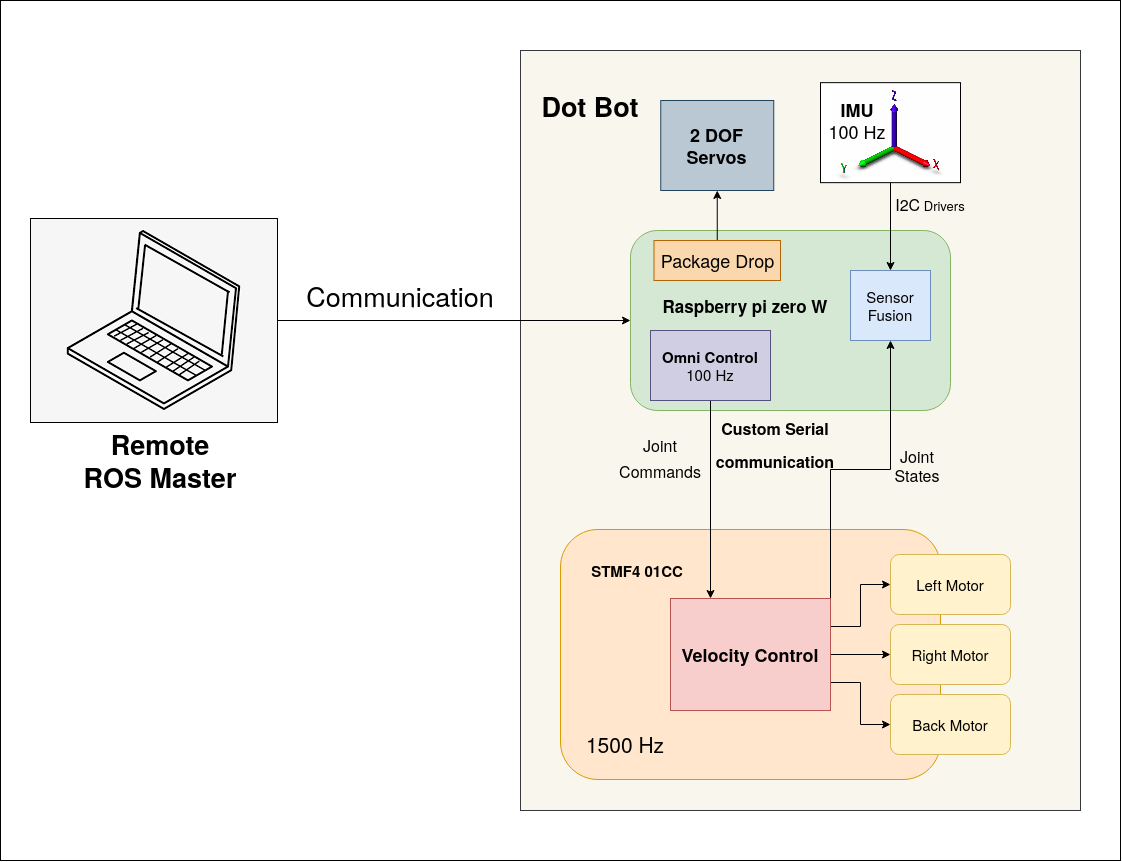
Figure 1: Control Mechanism
- Communication: Communication between the robot and the remote PC is established through ROS networking for multiple machines. The connection between the microprocessor and the microcontroller utilizes UART at a baud rate of 2,000,000.
- Pose Estimation: Pose estimation combines encoder and IMU data for odometry (odom to base frame) and employs external cameras for ground truth mapping (map to base frame).
- Controller: A velocity-based three-wheel omni-drive system operates at 100 Hz on the Raspberry Pi, with the microcontroller managing individual motors to execute the desired velocities. This setup facilitates seamless transition from simulation to real-world applications.
The complete implementation of the control architecture is available on our Swarm-Bot-Hardware GitHub repository.
Simulation
We have meticulously set up a comprehensive simulation environment that mirrors the real-world robot. This includes modeling the robot with 2DOF droppers visible atop each unit. Additionally, we configured Rviz to visualize the robots both in simulation and hardware environments.
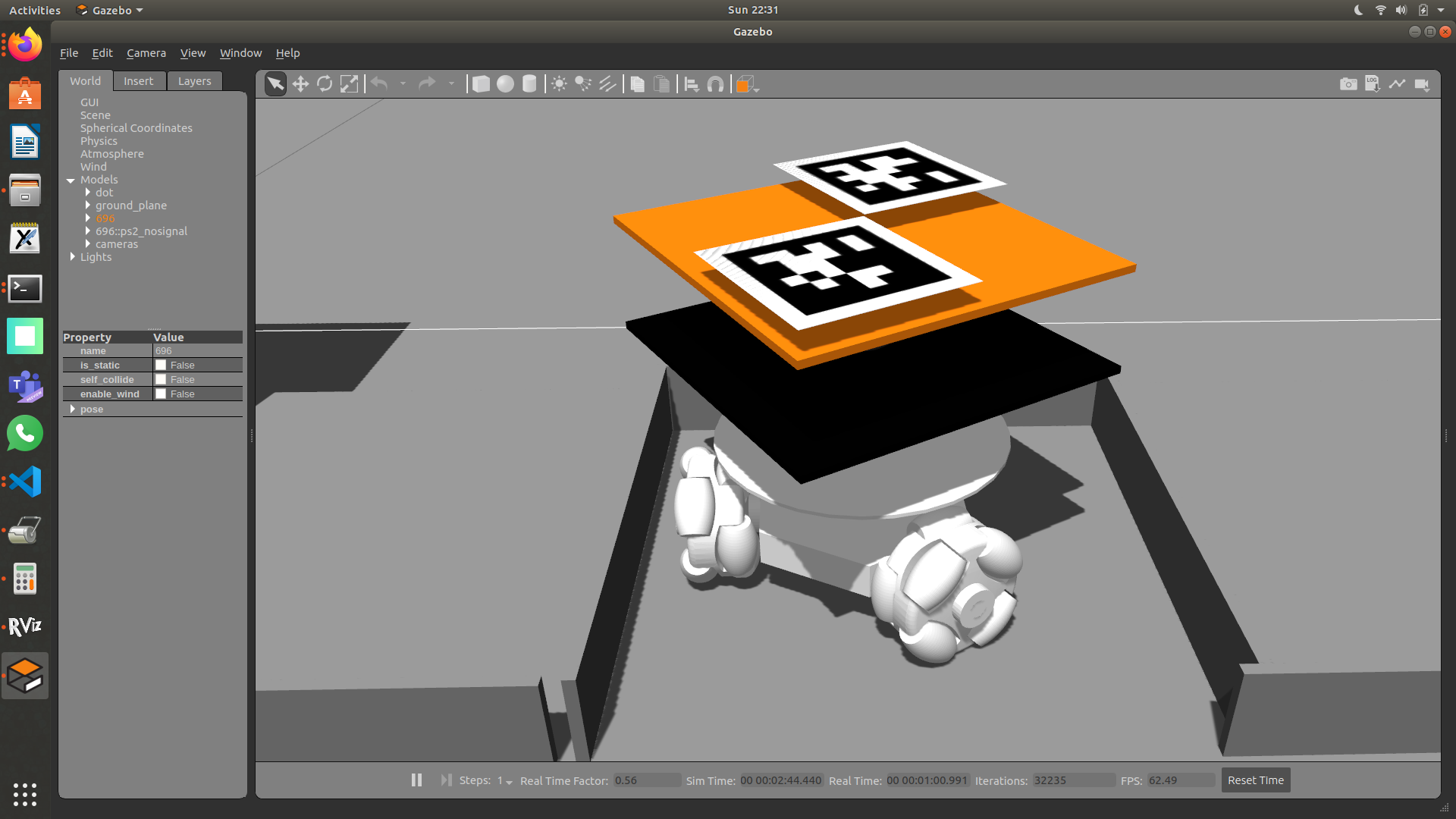
Figure 2: Robot Simulation in Gazebo
FlipKart Grid Challenge
The primary objective was to optimize package delivery paths. We employed the Continuous-CBS algorithm, making minor modifications to better suit our specific problem statement. Additionally, we integrated a Tracking PID controller to enhance trajectory tracing, ensuring robustness and compatibility with other algorithms and systems.
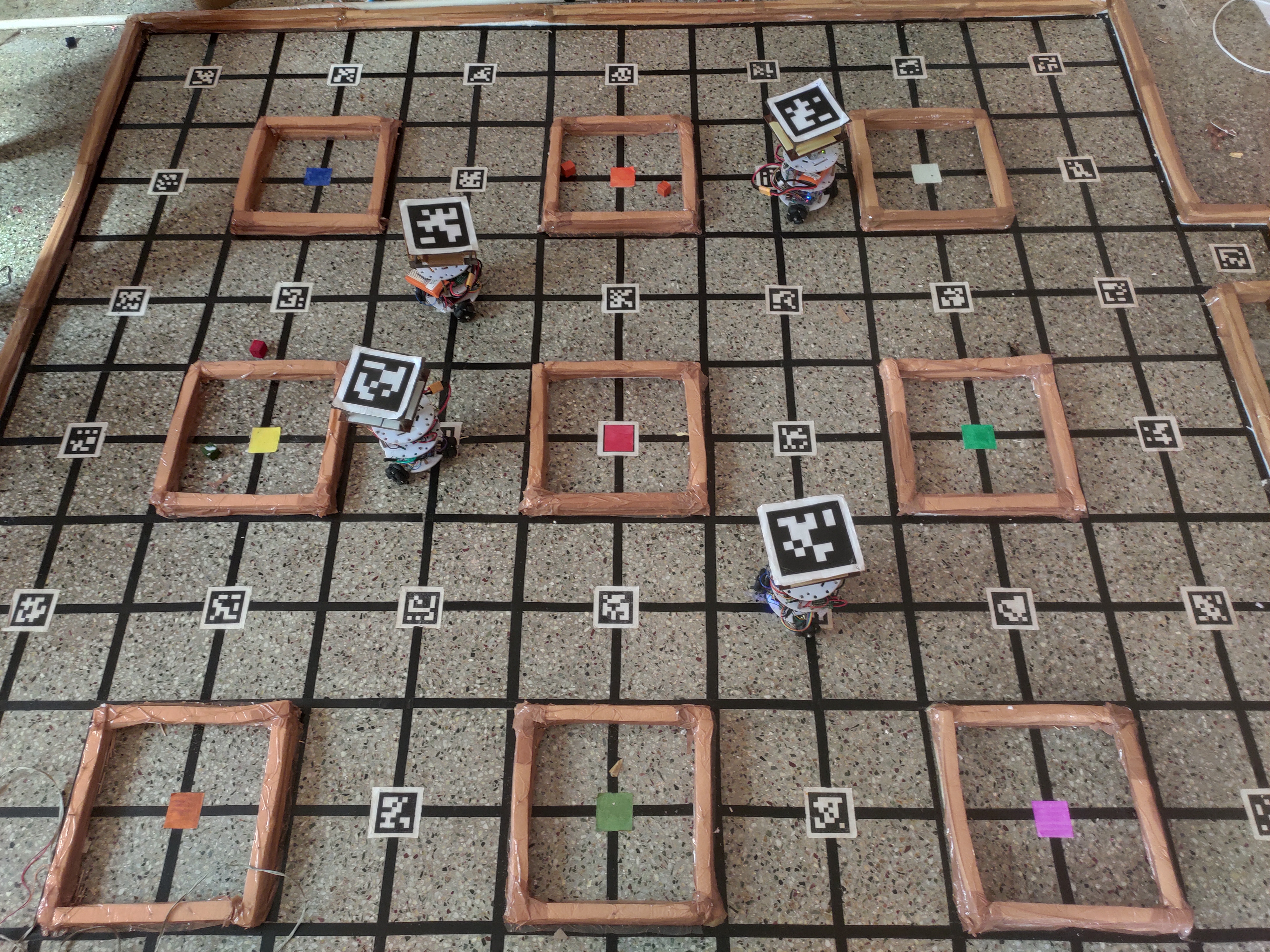
Figure 3: Arena Layout for Package Delivery
Our robot serves as a developmental platform for multi-agent research at the Indian Institute of Technology, Varanasi. Future enhancements include integrating LiDAR sensors and upgrading onboard computation to facilitate more real-world applications.
Below is a preliminary result showcasing the path planning algorithm with package dropping capabilities:
Figure 4: Project Demonstration